Thalassemia- A Genetic Disorder
- Chaitanya Ambike
- Apr 1, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Apr 2, 2022
What is a Genetic Disorder?
Every 6 out of 10 people have health problems associated with genetic mutations. Genetic disorders occur when a mutation affects your genes or when you have an insufficient amount of genetic material. Genes are made of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which contains the instructions for cell functions as well as the characteristics that distinguish you from everybody else.
As we know humans receive half of their genes from each of their biological parents and sometimes may inherit a gene mutation from one or both. Sometimes genes change as a result of problems within the DNA. This increases your chances of inheriting a genetic disorder. Some of these disorders can cause symptoms from birth, while others develop over time. Although there are many such disorders, today, we will attempt at familiarizing you with one particular one: Thalassemia.
What is Thalassemia and what are its symptoms? Red blood cells as we know carry oxygen throughout the body; hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that transports the oxygen. Thalassemia refers to a group of conditions that impair the body's ability to produce a normal amount of hemoglobin. It often causes severe anemia and other complications that occur over time. The symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale or yellowish skin, bone deformities, abdominal swelling, dark urine, and delayed growth and development.
What are the types of Thalassemia? Hemoglobin is made up of four protein chains — 2 alpha-globin and 2 beta-globin chains. As a result, we can differentiate thalassemia into 2 major types named after the defects that can occur in these protein chains:
1. Alpha-thalassemia: Four genes (i.e. 2 from each parent) are required to make one alpha globin protein chain. When one or more genes are missing, it causes alpha thalassemia.
2. Beta-thalassemia: There are normally 2 beta-globin genes (i.e. one from each parent)
. Beta thalassemia is caused when a mutation occurs in one or both of the beta-globin genes.
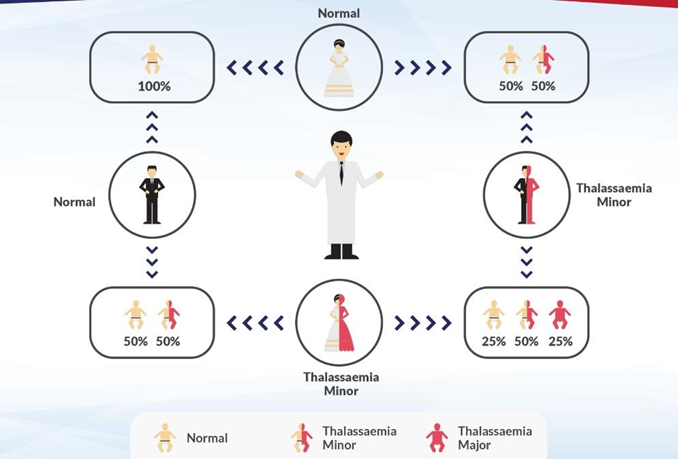
How is Thalassemia treated? Symptoms of thalassemia occur in infants when they are 6 to 24 months old. Standard treatment for this disorder is blood transfusion and iron chelation. The former includes inserting red blood cells into the body through a vein, every 4 months in alpha thalassemia patients and 2 to 4 weeks in beta-thalassemia patients. This is done in order to restore a normal level of hemoglobin. In turn, frequent blood transfusions can cause iron overload, which is extremely dangerous. Hence, the patients who receive frequent blood transfusions also require iron chelation. This involves the removal of iron from the body, which is usually done by taking pills. Bone marrow or stem cell transplant from a compatible donor can eliminate the need for lifelong blood transfusion. Are Genetic Disorders Treatable? Including thalassemia, most genetic disorders cannot be cured or prevented because it involves genes that we inherit. But in recent times with help of advanced technology, more than 600 genetic disorders have now become treatable. BIBLIOGRAPHY:
• Genetic conditions (healthywa.wa.gov.au) Written by: Amizhthini and Dhwaani



Comments